Wezen Translate is a powerful tool to manage your localization process and more specifically translation tasks. It is a module that connects users such as linguistic producers (translators, reviewers), production managers, and customers in order to work on localization projects. With this platform:
- Digital contents coming from a website or files are translated and reviewed by linguistic producers.
- Production managers can have a complete overview of ongoing and past projects.
- Customers can submit requests for translations, validate translated content and monitor their localization projects.
It was developed to streamline the localization process and to handle any content type. Each project is set up with specific workflows which guarantee high standards quality level before delivery.
It is composed of projects which gather users, content to be processed, and tools to perform the localization process. The figure below explains how Wezen handles the localization process.

1. Sending from the source environment
In the first step in the localization process, source content which needs to be localized from customers is imported into Wezen either automatically or via manual file upload. Depending on the customer's needs, there can be different types of content: websites, pages and assets, documents, product information, leaflets, application files, etc.). You can manually import content to Wezen via CODEX or API. Wezen can be also integrated to Adobe Experience Manager (AEM), Salesforce Commerce Cloud and Akeneo.
2. Conversion into translations tasks
For any source content that is received by Wezen, translation tasks are created. On Wezen, these translation tasks are called Translation Batches. Each translation batch contains content to be translated into a single target language. Therefore, if a source content needs to be translated into several languages, there will be several corresponding translation batches. They also contain attributes such as delivery time, contextual elements for linguistic producers, who it is assigned to, etc.
3. Management of the translation process
Wezen includes a powerful tool to manage translation tasks. In order to guarantee a well managed process, all the translation tasks follow the same project-specific predefined workflow. These tasks are then assigned to linguistic producer and customers who will manage each step of the translation process. The tasks can only be assigned to users whose mother tongue matches the target language of the translation batch.
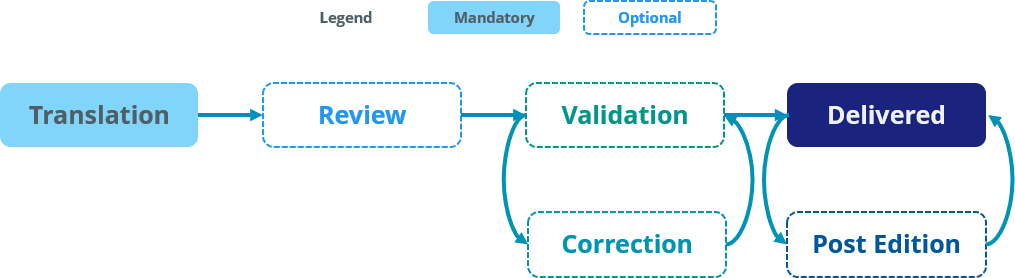
Usually, a typical workflow is the following: Translation, Review, Validation.
Steps such as Review, Correction, Validation and Post Edition can be added to or removed from the workflow, meaning that depending on projects, two examples of workflows could be: Translation, Validation or Translation, Review #1, Review #2, Validation.
4. Translation of the content
The content to translate is usually broken down into several pieces of text, such as titles, paragraphs, captions, product descriptions, etc. We call them Translation Units. These translation units are extracted and divided into smaller units called Segments. Segments are what linguistic producers translate into a target language.
For instance, on an eCommerce website, a product will represent a translation batch, the product name and description will represent translation units, and each sentence of the product description will be a segment.
Below, you can see on the left a subtitle below the image of the city of Paris. On the right, you can see the translation unit "content: 9 words" split into two segments ("Built for lovers..." and "Discover it!").

Wezen includes a translation workbench where linguistic producers can translate the source segments, called Translation Studio. This translation workbench comes with Computer Assisted Translation (CAT) tools that help linguistic producers. It is also possible to provide users with context elements in order to help them translate the content with as much accuracy as possible.
For example, on the image above, the image of Paris is an element of context and will be shown in the Translation Studio to the linguistic producer to help him with the translation task.
5. Delivery of the translated content
After it has gone through all the steps in the workflow, the translated content is then delivered back to the customer in the same format that it was imported in. The translated content is then automatically reintegrated into the customer's target content location.
6. Reporting
Lastly, Wezen allows customers, linguistic producers and project managers to monitor the localization process. Reporting tools are available and depending on their roles, users have access to different charts and statistics, such as average translation time, translation volume history, project workload status, linguistic producer's activity report, etc. These reporting tools enable strategic and data-driven decisions to improve the performance of the localization process on the platform.

